10 Proven Strategies for Mastering What Is Inventory Control
Introduction:
What is inventory control? This crucial question sits at the heart of efficient business operations. Inventory control is the systematic approach to sourcing, storing, and selling inventory—both raw materials (components) and finished goods (products). The goal of inventory control is to ensure that a company always has the right amount of inventory to meet customer demands without delay while minimizing the costs associated with holding and managing that inventory.
Understanding Inventory Control
What is inventory control? At its core, inventory control involves tracking inventory levels, orders, sales, and deliveries. It also includes the process of ordering and restocking inventory and controlling the quantity of products for sale. Inventory control is vital for maintaining the balance between supply and demand, which is essential for any business that deals with physical goods.
Effective inventory control ensures that a company can fulfill orders without overstocking or understocking. Overstocking ties up capital and increases storage costs, while understocking can lead to lost sales and dissatisfied customers. Thus, mastering inventory control is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and profitability.
The Importance of Inventory Control
Inventory control is essential for various reasons, including cost management, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Understanding what is inventory control and its importance can significantly impact a business’s success.
- Cost Management: Inventory control helps businesses reduce costs associated with excess inventory. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, companies can minimize storage costs, reduce waste from obsolete inventory, and free up capital for other investments.
- Customer Satisfaction: Effective inventory control ensures that products are available when customers need them, leading to higher customer satisfaction. Meeting customer demand promptly can result in repeat business and positive word-of-mouth, which are critical for growth.
- Operational Efficiency: Proper inventory control streamlines operations by reducing the time and effort needed to manage inventory. It also helps prevent disruptions in the supply chain, ensuring that production processes run smoothly.

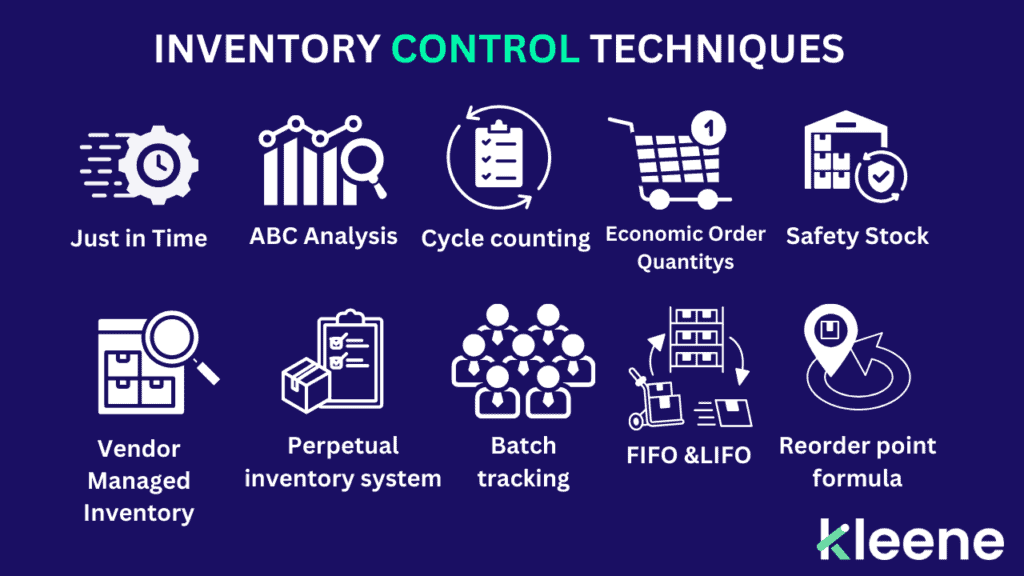
Key Techniques in Inventory Control\
There are several techniques that businesses can use to master inventory control. Each method offers unique advantages and can be tailored to fit specific business needs.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: The JIT method reduces inventory holding costs by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process. This approach minimizes excess inventory and reduces waste. However, it requires accurate demand forecasting and reliable suppliers.
- ABC Analysis: ABC analysis categorizes inventory into three classes based on their importance: A (high-value items with low frequency of sales), B (moderate value and frequency), and C (low-value items with high frequency of sales). This method helps prioritize inventory management efforts on the most critical items.
- Cycle Counting: Cycle counting involves regularly counting a subset of inventory items to ensure accuracy without disrupting operations. This technique helps identify discrepancies and maintain accurate inventory records.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): EOQ is a formula used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering and holding costs. This method helps balance the cost trade-offs and ensures efficient inventory management.
- You may also like: Unlocking Success: The 10 Most Powerful Inventory Formulas
- Safety Stock: Safety stock is the extra inventory held to mitigate the risk of stockouts caused by uncertainties in demand or supply. It acts as a buffer to ensure that there are sufficient products available to meet unexpected demand.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): VMI involves suppliers managing the inventory levels of their products at the customer’s location. This approach improves collaboration between suppliers and customers and ensures optimal inventory levels.
- Perpetual Inventory System: A perpetual inventory system continuously updates inventory records in real-time with every transaction, providing accurate and up-to-date inventory information. This method enhances inventory visibility and helps prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Batch Tracking: Batch tracking allows businesses to track groups of products with similar characteristics, such as production date or batch number. This technique is particularly useful for managing perishable goods and ensuring product quality and safety.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO) and Last-In, First-Out (LIFO): FIFO and LIFO are methods used to manage the order in which inventory is used or sold. FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first, while LIFO assumes that the most recently received inventory is sold first. These methods can impact cost of goods sold and inventory valuation.
- Reorder Point Formula: The reorder point formula helps determine the inventory level at which a new order should be placed to avoid stockouts. It considers factors such as lead time, demand rate, and safety stock.
The Limitations of ERP Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are commonly used for inventory control, but they come with limitations. Understanding what is inventory control helps to identify these limitations and seek more effective solutions.
- Limited Functionalities: ERP systems often have limited functionalities for specific inventory control needs. They may not provide the flexibility required to handle unique business processes or the capability to perform advanced inventory analyses.
- Complex Setup: Setting up an ERP system can be complex and time-consuming. It requires extensive configuration and customization to meet the specific needs of a business, which can delay implementation and increase costs.
- Dependence on Accurate Data: ERP systems rely heavily on accurate data entry. Any errors in data input can lead to inaccurate inventory records and poor decision-making. Ensuring data accuracy requires significant effort and vigilance.
- Inadequate Reporting: The reporting capabilities of ERP systems are often limited. They may not provide the detailed and customizable reports needed for effective inventory management. Businesses may need to rely on additional tools or manual processes to generate the necessary reports.
Integrating Data into a Data Warehouse
One way to overcome the limitations of ERP systems is by integrating inventory data into a data warehouse. A data warehouse is a central repository that consolidates data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of the business.
- Accurate Forecasting: By integrating data into a data warehouse, businesses can ensure that inventory data is accurate and up-to-date. This enables more reliable demand forecasting and inventory planning.
- Comprehensive Analysis: A data warehouse allows for comprehensive analysis of inventory data, independent of the ERP system’s limitations. Businesses can perform advanced analyses and gain deeper insights into their inventory management processes.
- Reduced Dependence on ERP Setup: Integrating data into a data warehouse reduces dependence on the ERP system’s setup and configuration. This ensures that inventory data is accurate regardless of how well the ERP system is configured.
- Enhanced Reporting: Data warehouses offer enhanced reporting capabilities. Businesses can generate detailed and customizable reports that provide actionable insights into inventory performance. This helps in making informed decisions and optimizing inventory control.

The Advantages of Tailored Solutions
In addition to integrating data into a data warehouse, businesses can benefit from tailored inventory control solutions that meet their specific needs.
- Flexibility and Customization: Tailored solutions provide the flexibility to adapt to a business’s unique processes and requirements. Unlike black-box solutions that sit on top of ERPs, tailored solutions can be customized to fit seamlessly with the existing tech stack and sales channels.
- Specific Reporting: Tailored solutions offer specific reports relevant to the business’s unique use case. This eliminates the need for additional spreadsheets and manual data entry, ensuring that reports are accurate and comprehensive.
- Better Integration: Tailored solutions integrate better with other systems and processes, providing a cohesive inventory management system. This ensures that inventory control is aligned with the overall business strategy and operations.
- Improved Efficiency: By using a tailored solution, businesses can improve the efficiency of their inventory management processes. This leads to reduced costs, better customer satisfaction, and enhanced operational performance.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Examining real-world examples and case studies can provide valuable insights into effective inventory control practices and further elucidate what is inventory control.
- Walmart: Walmart, one of the largest retailers in the world, uses advanced inventory management techniques to maintain optimal inventory levels. The company leverages technology, such as RFID and data analytics, to track inventory in real-time and ensure product availability.
- Toyota: Toyota is renowned for its Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory system, which minimizes inventory holding costs and reduces waste. The company’s lean inventory management practices have set a benchmark for the automotive industry.
- Zara: Zara, a global fashion retailer, uses a responsive inventory control system to quickly adapt to changing fashion trends. The company’s inventory management strategy allows it to deliver new designs to stores within weeks, reducing the risk of overstocking.
Future Trends in Inventory Control
As technology continues to evolve, new trends are emerging that will shape the future of inventory control. These trends will redefine what is inventory control and how it is practiced.
- Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics will play a significant role in inventory control, streamlining processes and reducing manual labor. Automated warehouses and robotic picking systems will enhance efficiency and accuracy.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can provide transparent and secure tracking of inventory throughout the supply chain. It ensures data integrity, reduces fraud, and enhances traceability.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics will become more sophisticated, enabling businesses to anticipate demand with greater accuracy. This will lead to more efficient inventory planning and reduced stockouts.
- Sustainable Inventory Management: Sustainability will become a key focus in inventory control. Businesses will adopt eco-friendly practices, such as reducing waste, optimizing transportation, and sourcing sustainable materials.
Conclusion
What is inventory control? It is the systematic approach to managing inventory to ensure that a business can meet customer demand while minimizing costs. Mastering inventory control involves a combination of advanced techniques, leveraging technology, and overcoming the limitations of traditional ERP systems.
By integrating data into a data warehouse and adopting tailored solutions, businesses can achieve accurate forecasting, comprehensive analysis, and enhanced reporting. These strategies enable businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance operational efficiency.
Understanding what is inventory control and its impact on a business is crucial for success in today’s competitive market. By implementing effective inventory control practices, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and achieve long-term growth.
Using Kleene for Retail Inventory Management
Kleene is a leading AI-powered inventory management solution trusted by data-driven companies worldwide. With its advanced demand forecasting capabilities and comprehensive data analysis tools, Kleene gives retailers everything they need to confidently optimise inventory levels, reduce costs and improve operational efficiency. It’s a must-have platform for retail inventory management.
With Kleene’s predictive analytics and actionable insights, retailers can find new opportunities for growth around every corner. AI-powered retail inventory management offers immense potential for retailers to find ways to optimise their supply chain operations and drive enhanced customer satisfaction. In adopting a few best practices and leveraging a platform like Kleene, retailers can stay ahead of the curve.
Download our free e-book on how CFOs can master working capital in retail.
You may also like:
7 Unmissable Ways Inventory Tracking Management Outperforms ERP Systems
7 Powerful Tips for Small Business Inventory Management to Maximise Efficiency
Boost Your Inventory Turnover Ratio with These 5 Proven Strategies
The Ultimate Guide to Inventory Management Software: Top Solutions for 2024
7 Powerful Insights on What is Inventory in Accounting
Frequently Searched Questions about Inventory Control
1. What is inventory control in simple terms?
Inventory control is the process of managing a company’s stock to ensure it has the right products in the right quantity to meet customer demand while minimizing costs.
2. How does inventory control affect a business?
Effective inventory control helps a business reduce costs associated with excess inventory, avoid stockouts, and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability.
3. What are the main techniques used in inventory control?
Key techniques include Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory, ABC analysis, cycle counting, and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ).
4. What are the limitations of ERP systems in inventory control?
ERP systems often lack detailed reporting capabilities and require extensive setup and configuration, which can be costly and time-consuming.
5. How can integrating data into a data warehouse improve inventory control?
Integrating data into a data warehouse ensures accuracy and comprehensiveness, independent of ERP system setup, allowing for better forecasts and decision-making.
6. Why are tailored solutions better than standalone systems for inventory control?
Tailored solutions offer flexibility, specific reporting, and seamless integration with other business systems, improving efficiency and accuracy.
7. What is the difference between inventory control and inventory management?
Inventory control focuses on tracking and managing stock levels, while inventory management encompasses the broader process of sourcing, storing, and selling inventory.
8. How does technology enhance inventory control?
Technologies like inventory management software, barcode and RFID systems, and AI-driven analytics enhance accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making in inventory control.
9. What are the benefits of advanced inventory control techniques like VMI and lean inventory management?
Advanced techniques like Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) and lean inventory management improve collaboration, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency in inventory control.
10. What future trends will impact inventory control?
Trends like automation, blockchain technology, predictive analytics, and sustainable inventory management will shape the future of inventory control, driving greater efficiency and transparency.
11. What is inventory control and how important is it to be efficient?
Inventory control is the systematic approach to managing inventory to ensure that the right products are available at the right time while minimizing costs. Efficiency in inventory control is crucial as it helps reduce operational costs, avoid stockouts and overstock situations, and enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely product availability.



